"Oh those genes
are the little machines
that cause my body
to change in my teens."
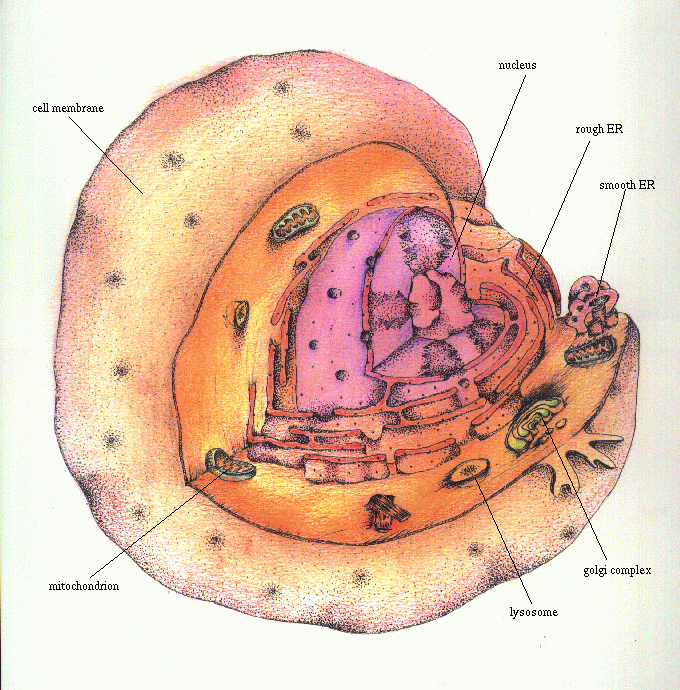
We use the term genome to refer to all of the alleles possessed by an organism (or by a population, species, or larger taxonomic group). While the amount of DNA for a diploid cell is constant within a species, the differences can be great between species.

Humans have 3.5 X 109 base pairs, Drosophila has 1.5 X 108, toads have 3.32 X 109, and salamanders have 8 X 1010 base pairs per haploid genome.
Genetics crucial role in life.
How would you define–a gene or–genes & what they do? Evelyn Fox Keller may disagree!